Posted on May 1, 2024
Every state has a minimum amount of car insurance you must buy to satisfy financial responsibility laws. Liability insurance is the main mandated coverage. It covers damage and injuries you cause to others in an accident.
The most common minimum limits for liability are $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident for bodily injury and $25,000 for physical damage. But your state’s requirements may be higher or lower. The key to figuring out how much car insurance you need is knowing your state’s requirements and examining your specific situation.
How Much Car Insurance Do I Need?
Beyond what is required by state car insurance laws and your lender, you need enough car insurance to pay for injuries, property damage and lawsuits that may arise from an accident if you don’t have enough savings to pay for them otherwise. And even if you do have the savings, can you afford to spend it all on a car accident? If you’re like most people, the answer to that question is no.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners recommends enough car insurance to:
- Comply with state laws
- Satisfy your lender
- Protect your assets
What Car Insurance Coverage Do I Need?
Most states require that car owners buy liability car insurance, but coverage requirements vary by state. Depending on where you live, you may be required to buy additional types of car insurance, such as uninsured motorist coverage, personal injury protection or medical payments coverage.
Drivers who lease or finance their vehicles are usually required to buy collision and comprehensive insurance.
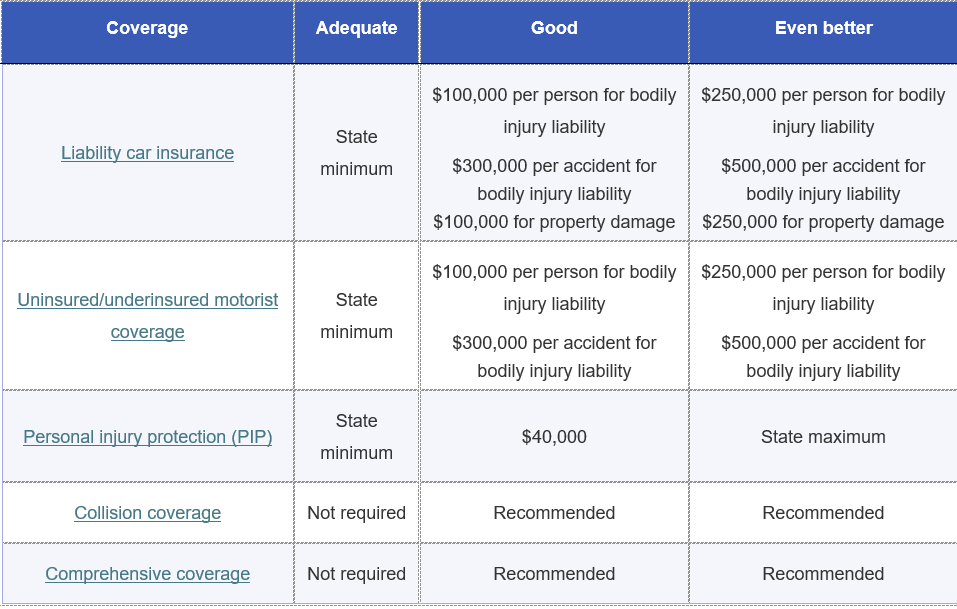
Here are common car insurance coverage options and recommended coverage amounts for each. These are general recommendations, so it is important to assess your personal financial situation to determine your needs.
Car Insurance Requirements by State
Every state has a financial responsibility law for vehicles, which most drivers satisfy by buying car insurance.
The minimum amount of auto insurance you need to buy varies by state. But no matter where you live, liability car insurance—which covers damage and injuries you cause others in an accident—is the main required coverage. The minimum car insurance required by your state is important to know, but this amount may not be adequate for your needs.
Which States Don’t Require Car Insurance?
While requiring car insurance is the norm, three states are unique in the choices you have.
- New Hampshire does not require car insurance, but if you’re in an at-fault accident you must prove you have adequate funds to fulfill the state’s financial responsibility law. This could include buying car insurance.
- South Carolina law allows you to legally drive without auto insurance if you meet certain qualifications and pay $600 to register an uninsured vehicle.
- Virginia permits you to pay a fee of $500 to register your car as an uninsured motor vehicle.
Choosing to go without car insurance in any of these three states leaves you personally responsible for paying for damages to property or injuries to people if you cause an accident.
How to Estimate Car Insurance Costs
Compare car insurance quotes from multiple insurance companies to get a reliable estimate of what car insurance will cost for your needs. Factors like your age, type of vehicle, coverage amount, deductibles, driving history and location will be used in determining your costs.
Is Minimum Car Insurance Coverage Enough?
At the very least, you must buy your state’s minimum car insurance requirements. But state minimums are usually woefully inadequate and won’t provide any coverage for your own car’s repair bills. If you want better coverage, you’re going to need to buy more than the minimum requirements.
With a basic knowledge of the main types of car insurance, you can put together a good policy that fits your specific insurance needs.
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage
Liability Insurance
Liability car insurance covers injuries and property damage suffered by others if you’re at fault for an accident. It also covers your legal defense and any settlements or judgments if you’re sued because of an accident.
Liability car insurance includes two different types of coverage packaged together:
- Bodily injury liability pays for injuries to other drivers, their passengers and any hurt pedestrians if you’re at fault for an accident.
- Property damage liability pays for damage to another individual’s property, including their vehicle, if you cause an accident.
Here are a few examples of what liability insurance covers:
- You rear end another car at a traffic light and cause damage.
- You crash into a neighbor’s fence.
- You are responsible for a car accident and the other driver is injured.
Nearly every state has a minimum liability insurance requirement, with the exception of New Hampshire, South Carolina and Virginia (although these states have some liability insurance requirements under certain conditions).
For example, in California, you need to have liability insurance with at least $15,000 for bodily injury to one person, $30,000 for bodily injury to multiple people in a single car accident, and $5,000 for property damage (written as 15/30/5).
But here’s the problem: These amounts are insufficient if you cause a serious car accident. If you total someone else’s car, $5,000 of property damage won’t get you very far. And if you’re at fault for a car accident with multiple injuries, medical expenses can quickly exceed $30,000. You’ll be on the hook for any amount above your coverage limits.
How much liability insurance should I buy?
A good rule of thumb is to buy enough liability insurance to cover what you could lose in a lawsuit against you if you cause a car accident. In California, a policy with 250/500/100 would be a much better choice than the state minimum.
For extra liability insurance above your base auto and home insurance policies, consider getting an umbrella insurance policy. You can buy an additional $1 million (or more) in liability coverage through an umbrella policy for a relatively inexpensive amount.
Uninsured Motorist Insurance
Uninsured motorist (UM) and underinsured motorist (UIM) insurance pay for your medical bills if someone crashes into you and they do not have liability insurance or not enough. Uninsured motorist coverage is required in some states and optional in others. In states where UM is optional, you can typically reject the coverage in writing.
If UM is available in your state, this is good coverage to have. UM coverage pays for:
- Medical expenses for you and your passengers.
- Lost wages if you cannot work because of injuries suffered in a car accident.
- Funeral expenses.
- Pain and suffering of you or your passengers.
- Your vehicle damage (depending on your state), if you have purchased uninsured motorist property damage coverage.
Uninsured motorist insurance does not pay anything to the uninsured driver who caused the accident. They’re on their own.
How much uninsured motorist coverage should I buy?
You’ll typically need to purchase UM in amounts that match your liability insurance. For example, if you have 250/500/100, you’ll need to buy the same amount of UM coverage.
Collision and Comprehensive Insurance
If you want insurance for your car repair bills, you need collision and comprehensive insurance. Often sold together, they cover a range of problems like car accidents, car theft, vandalism, collisions with animals, falling objects, fires, floods and hail damage.
If you have a car loan or lease, your lender or leasing company will most likely require you to buy both of them.
How much collision and comprehensive insurance should I buy?
Both coverage types will cover the cost to repair or replace your vehicle if it is damaged by a problem covered by the policy. If you want to cut down on costs, select a higher deductible amount, which is the amount you’ll pay out of pocket toward repairs if you file an insurance claim. For example, a $1,000 deductible will result in slightly cheaper premiums compared to a $500 deductible.
Personal Injury Protection
Personal injury protection (PIP) covers medical bills for you and your passengers no matter who caused the car accident. It also pays for other expenses like lost wages, funeral expenses and replacement services you can’t do because of injuries, like cleaning services or child care.
Some states require PIP as part of its “no-fault auto insurance” laws, while in other states you can buy PIP as an optional coverage type.
How much PIP insurance should I buy?
PIP rules vary by state and it’s not sold in all states. For example, for Florida car insurance, PIP options range from basic to extended:
Basic Florida PIP covers 80% of your medical bills and 60% of lost wages and replacement services
Extended Florida PIP covers 100% of medical bills and 80% of lost wages and replacement services
If PIP is optional in your state, you can decline it if you have a good health insurance plan. But PIP has some perks your health insurance won’t provide, such as reimbursement for services and lost wages.
Medical Expenses Coverage
Medical expenses coverage is also known as medical payments coverage and often referred to as “MedPay.” It’s similar to PIP in that it pays for medical bills and other expenses for you and your passengers, no matter who caused the car accident. MedPay is required in some states. For example, MedPay is required if you buy car insurance in Pennsylvania, Maine and New Hampshire.
How much MedPay should I buy?
In states where MedPay is available, it’s usually sold in small amounts of coverage that often range between $1,000 and $5,000.
Optional Car Insurance Coverage Types
Liability insurance, uninsured motorist coverage, medical payments, and collision and comprehensive insurance are a good foundation for a car insurance policy. But you might need a few additional coverage types to fill in some gaps. Here are some to consider.
- Gap insurance. If your car is totaled due to a problem covered by your policy, such as a car accident or fire, gap insurance covers the difference between the actual cash value of your car and how much you owe on the loan or lease. For example, if you have $15,000 outstanding on your loan but your car’s value was $13,000, this coverage pays the $2,000 gap.
- Rental reimbursement insurance. If your car is being repaired due to a problem covered by your policy, rental reimbursement insurance pays for a rental car or substitute transportation, such as train and bus fare, during repairs.
- Roadside assistance insurance. If your car breaks down or you run into another problem (like locking your keys in your car), roadside assistance insurance pays for services like a tow truck, jump-start, fuel delivery or a locksmith.
How to Buy Car Insurance
The average cost of car insurance is $1,601 per year for a policy with liability, collision and comprehensive insurance, according to a Forbes Advisor analysis of car insurance costs. But don’t focus strictly on cost when you’re looking for a car insurance policy.
Auto insurance companies all calculate their rates differently, resulting in a wide range of prices—sometimes by thousands of dollars a year. It’s smart to compare car insurance quotes from multiple companies. You can get free quotes online or by calling an independent agent in your area.
Make sure you ask about car insurance discounts. Insurance companies offer many types of discounts to attract customers—everything from good driver discounts, car safety discounts, and multi-policy discounts to discounts for paying in full or going paperless
Finally, consider a company’s customer service. The best car insurance companies pair competitive prices with good customer service. If you get into a car accident, you want to be sure your insurance company will make the insurance claim process go as smoothly as possible.
Source: https://www.forbes.com/advisor/car-insurance/how-much-car-insurance-do-you-need/


Recent Comments